Stop Tilting At Windmills
Brandon Konkle <brandon@lincolnloop.com>
Yann Malet <yann@lincolnloop.com>
DjangoCon 2011 Portland, OR
Target Audience
- You have built one or more successful application
- You need to scale it to reach a larger audience
Agenda
Performance Testing
- Debug Toolbar
- Debug Logging
- Continuous testing
Load Testing
- Jmeter
- Command-line tools
This talk will not discuss
-
How to optimize django apps
- Optimizing queries
- Caching
- etc...
-
How scale your infrastructure
Django community's focus is evolving
Where are we coming from?
- 2008 - Building reusable apps
- 2009, 2010 - Testing and continous integration
Where are we (hopefully) going?
- Larger scale
- Better performance
Tilting at Windmills
Like the brave but misguided Don Quixote we often charge after performance problems we think are monstrous,
but turn out to be just minor issues.

Example Django-CMS Site
We built few utilities on top of django-cms to:
- Create a dummy web site on demand
- Get the list of urls for the django-cms pages
Performance Testing
Performance Testing
"You can't manage what you don't measure"
What are we looking for?
- Time to load a page
- Number of queries per page
- Time taken by the queries
- Number of cache hits/misses
- Time spent waiting for external services
Response Time
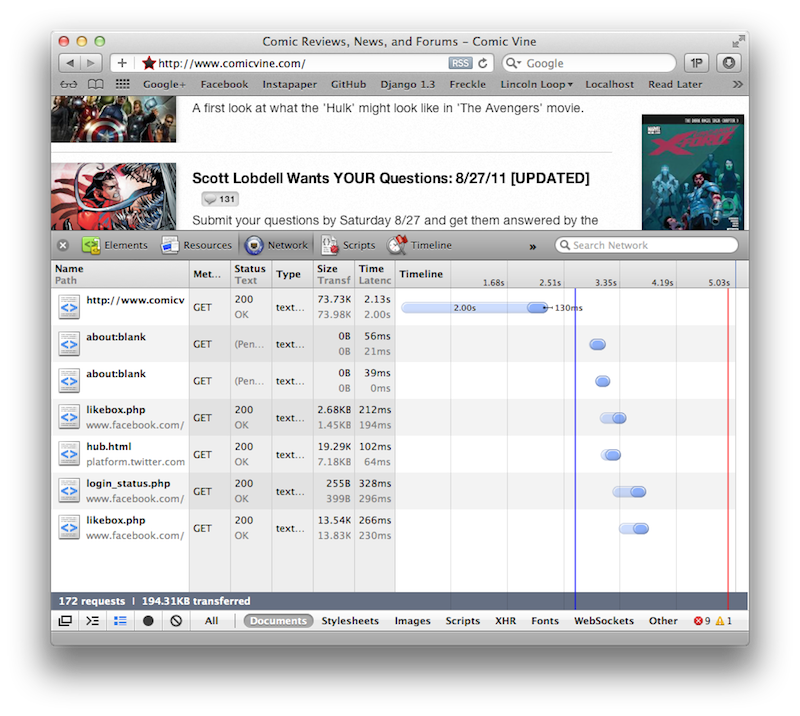
Response Time
Pros
- No setup.
- Closest to the user experience.
Cons
- It doesn't measure the internals of your application.
- It's a simple good/not good evaluation, with no clues about why.
Django Debug Toolbar
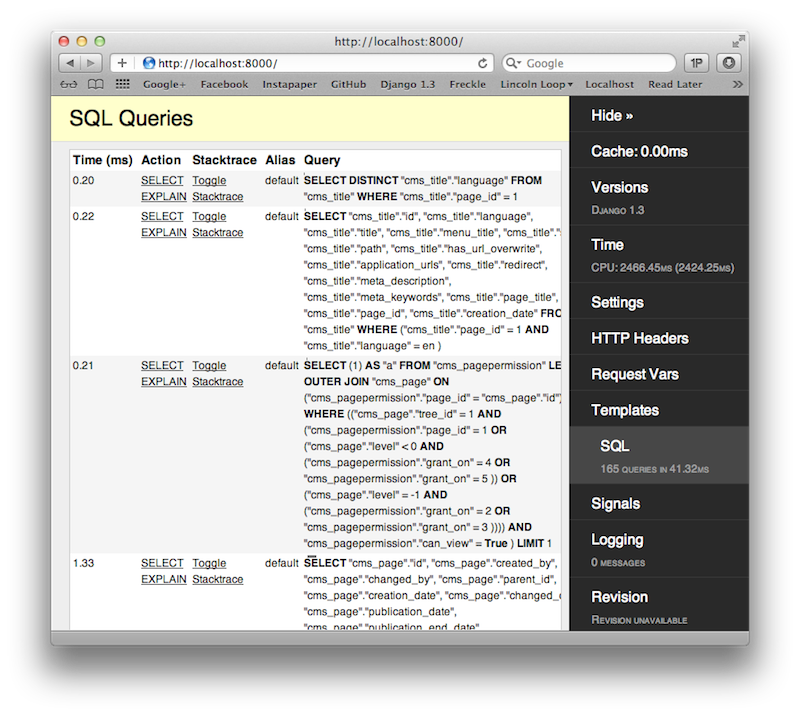
Django Debug Toolbar
Pros
- Provides a variety of information about what is going on inside.
Cons
- Requires a third party application and some configuration.
- It's on demand.
- No history.
Django Debug Logging
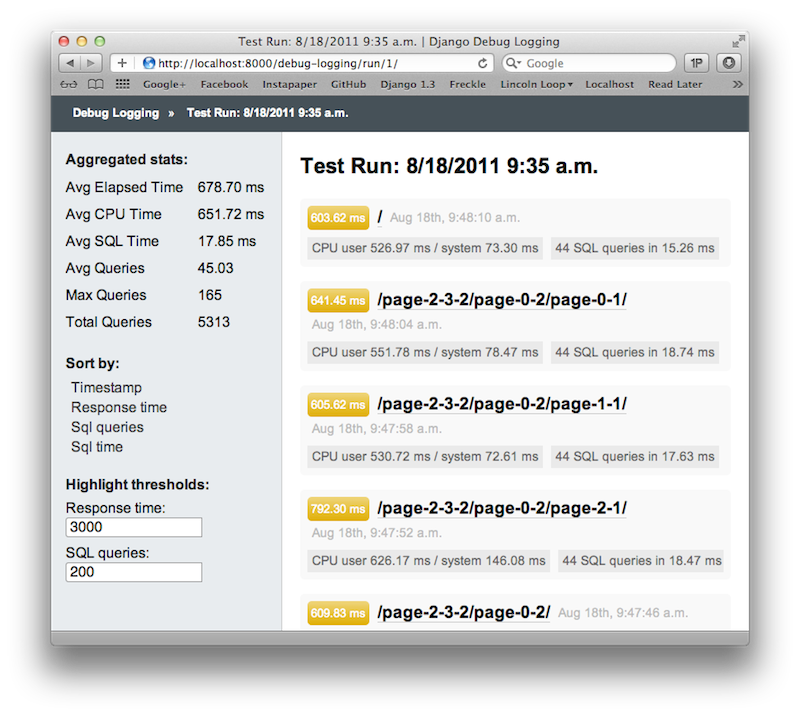
Django Debug Logging
Pros
- Automated test covering a set of URLs
- Optimised for history tracking
- Repeatable process
- Provides aggregated data
Cons
- Young project
- Requires another third party application and more configuration.
Still A Work In Progress
At this stage it is a proof-of-concept. There are few outstanding issues and pending features.
- Better integration with django-debug-toolbar
- Support configurable log handlers, instead of just the database handler
- Optionally use unit tests instead of just url lists
Continuous Testing
Why?
- Helps narrow down the origin of performance problems
- Performance issues can't always be easily predicted
- Identify issues before they impact production
How?
- Manually run performance test throughout the day
- Run periodically with cron
- Integrate with a tool like Jenkins
Load Testing
Load Testing
- Taking your entire application infrastructure into account.
- Understanding how your performance changes under stress and over time.
- Creating realistic test plans that imitate real life traffic.
What are we looking for?
Database
- Handling numerous queries in parallel
- Types of queries running at the same time
Caching
- Cache key expiration
- Cache size and key eviction
What are we looking for? (Cont'd)
Servers
- Memory utilization and swapping
- CPU load averages
- Balancing load effectively between database servers, app servers, utility servers, etc.
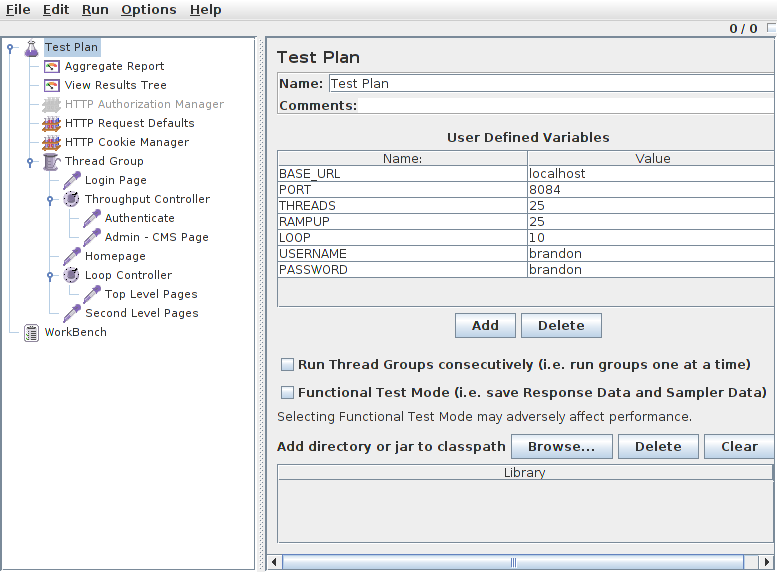
Jmeter
- Use a GUI to plan out a load test with a huge variety of highly configurable components.
- Set up samplers for each view your users will access.
- Create text files with sample data that can be read by each sampler.
- Use post-processors to retrieve data from your responses, such as CSRF keys.
- Authenticate a Django user by taking the CSRF key from a GET request, then POSTing it along with your credentials.
- Use throughput controllers to define the percentage of traffic on each request type.
Jmeter UI
jmeter -p user.properties
Jmeter CLI
jmeter -n -p user.properties -t windmill_plan.jmx -l results.jtl
Anatomy of a POST
Working around CSRF protection
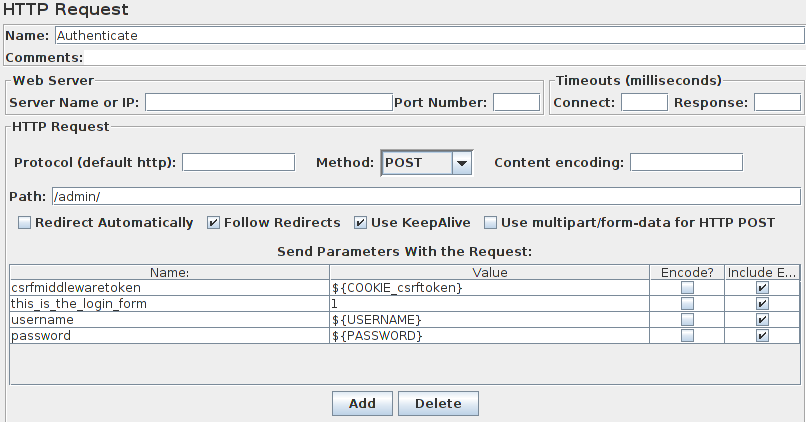
CSRF - This type of attack occurs when a malicious Web site contains a link, a form button or some javascript that is intended to perform some action on your Web site, using the credentials of a logged-in user who visits the malicious site in their browser.
Command-Line Tools
- htop - An amplified version of top to review load averages, memory utilization, swapping, etc.
- dstat - Shows a variety of information about cpu, memory, disk, and network usage.
- pg_top, mtop - Displays databases statistics and the process list, allowing you to view details about individual queries.
- memcache-top - Retrieves statistics from multiple memcached instances, such as space used/free, hit percentage, evictions.
Questions?
Brandon Konkle - @bkonkle
Yann Malet - @gwadeloop
Ground Kontrol
Lincoln Loop is hosting a private party for DjangoCon attendees at Ground Kontrol, from 9 to 11 pm Wednesday evening.
